Transmission of Scabies: How It Spreads
Transmission of Scabies: How It Spreads
Reader, have you ever wondered how easily scabies spreads? It’s a common concern, and understanding the transmission of scabies is crucial for prevention. **Scabies is a highly contagious skin infestation.** **It’s not just about cleanliness; anyone can contract it.** As someone who has extensively analyzed the transmission of scabies, I’m here to provide you with comprehensive information on how this pesky mite spreads.
This deep dive will equip you with the knowledge to protect yourself and others. We’ll explore the various ways scabies is transmitted, debunking common myths and offering practical prevention strategies. Let’s delve into the world of scabies transmission and empower you to take control of your skin health.


The most common way scabies spreads is through direct, prolonged skin-to-skin contact. This includes holding hands, hugging, and, most notably, sexual intercourse. The longer the contact, the higher the risk of transmission.
Infected individuals can transmit scabies even if they don’t show symptoms yet. This makes early detection and treatment crucial for containing outbreaks. This skin-to-skin transmission makes scabies especially prevalent in crowded living conditions.
Think about situations like crowded public transportation or close contact sports. These environments increase the risk of transmission. Therefore, awareness and preventative measures are paramount.

While less common than direct skin-to-skin contact, scabies can also spread through shared items. These items include bedding, towels, and clothing. The mites can survive for a short period, typically 24-36 hours, off a human host.
This means that sharing these items with an infected person can lead to transmission of scabies. It’s important to wash potentially contaminated items in hot water and dry them on high heat.
This will effectively kill the mites and minimize the risk of transmission. Be particularly cautious with items that come into close contact with the skin, such as bedding and towels. Regularly washing these items is crucial, especially in households where scabies is present.

Scabies in Children
Children are particularly vulnerable to scabies infestations due to their close physical interaction with others in schools and daycare centers. Outbreaks in these settings are common, emphasizing the importance of prompt diagnosis and treatment. Parents should be vigilant in checking their children for any signs of scabies.
Early detection and treatment can prevent widespread transmission within families and communities. Educating children about good hygiene practices, like not sharing personal items, can also play a role in prevention. Implementing these measures can significantly reduce the spread of transmission of scabies.
Remember to encourage frequent handwashing among children. This simple habit can make a big difference in preventing the spread of scabies and other infectious diseases.
Scabies in the Elderly
The elderly population, especially those in nursing homes or assisted living facilities, are also at increased risk. This is due to their potentially weakened immune systems and close living quarters. The transmission of scabies can spread rapidly in these settings.
Implementing preventive measures and having protocols for early detection and treatment are vital. Regular skin checks and prompt medical attention are essential to controlling outbreaks and protecting this vulnerable population. This proactive approach minimizes the disruption caused by scabies outbreaks.
Caregivers should be educated on how to identify and manage scabies to further limit its spread. This education can be instrumental in preventing widespread infestations within these facilities.
Scabies in Immunocompromised Individuals
People with weakened immune systems are at greater risk of developing a more severe form of scabies called crusted scabies. Crusted scabies, also known as Norwegian scabies, is characterized by thick, crusty skin lesions containing a high number of mites. This makes it highly contagious.
Early diagnosis and aggressive treatment are critical to prevent widespread transmission of this severe form of scabies. Extra precautions should be taken to prevent transmission, including isolation and meticulous disinfection of the environment. These measures minimize the risk of further spread.
Healthcare professionals should be particularly vigilant when treating immunocompromised individuals with scabies. They should closely monitor the patient’s response to treatment and adjust the approach as needed.
Scabies Myths and Misconceptions
Several myths surround scabies transmission, contributing to its spread. One common misconception is that scabies is only transmitted through sexual contact. While sexual contact is a route of transmission, it’s not the only one.
Another myth is that scabies is a sign of poor hygiene. This is untrue, as scabies can infest anyone regardless of their cleanliness habits. Understanding the facts about transmission of scabies is crucial for effective prevention.
Lastly, some believe that pets can transmit scabies to humans. While animals can have their own type of mange, it’s not the same as human scabies and is not easily transmitted between species. These clarifications are essential for understanding the transmission of scabies.
Preventing the Transmission of Scabies
Preventing the transmission of scabies involves a combination of strategies. Regular handwashing, especially after contact with potentially infected individuals or items, is paramount.
Avoiding sharing personal items like bedding, towels, and clothing is also essential. Regularly washing and drying these items at high temperatures helps to kill any mites that may be present.
If someone in your household is diagnosed with scabies, it’s crucial to treat all household members simultaneously, even if they don’t show symptoms. This helps prevent reinfestation and further spread of the mites. Early and comprehensive treatment is essential for effective control.
Diagnosing and Treating Scabies
If you suspect you have scabies, it’s crucial to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment. A doctor can diagnose scabies by examining your skin and potentially taking a skin scraping to confirm the presence of mites or their eggs.
Treatment typically involves prescription scabicide creams or lotions that are applied to the entire body from the neck down. These medications effectively kill the mites and their eggs, resolving the infestation. It’s important to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully and complete the entire treatment course, even if your symptoms improve.
It’s important to note that itching may persist for several weeks after treatment, even if the mites are eradicated. This is due to an allergic reaction to the mites and their waste products. Your doctor may recommend additional treatments for persistent itching. This ensures complete resolution of the infestation and its associated symptoms.
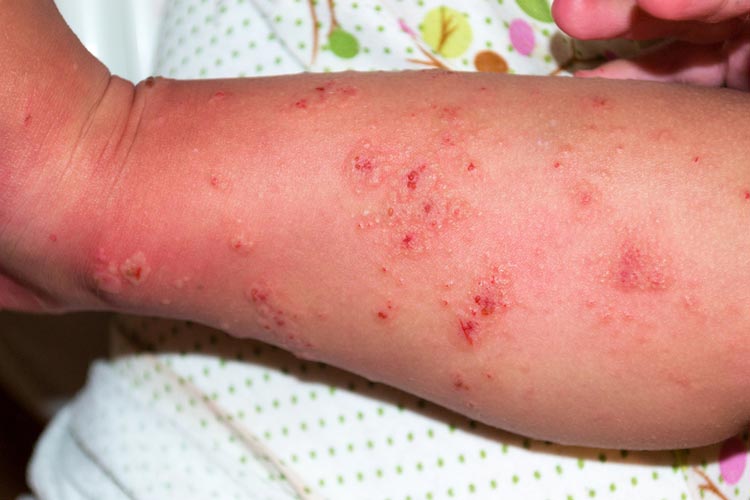
Table: Comparing Common Scabies Symptoms
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Intense Itching | Often worse at night |
| Rash | Pimple-like bumps or burrows |
| Sores | Can develop from scratching |
| Thick Crusts (Crusted Scabies) | Seen in severe cases |
FAQ: Common Questions About Scabies Transmission
How long can scabies mites survive off a human host?
Scabies mites can typically survive for 24-36 hours off a human host.
Can I get scabies from shaking hands?
While less common than prolonged skin-to-skin contact, brief contact like shaking hands can potentially transmit scabies, especially if the infected person has a high number of mites.
Can I get scabies from my pet?
No, the type of mange that affects animals is different from human scabies and is not easily transmitted between species.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Scabies Transmission
Understanding the transmission of scabies is key to preventing its spread. From skin-to-skin contact to shared items, we’ve explored the various pathways of transmission. By understanding these pathways and implementing preventative measures, you can effectively protect yourself and others.
We’ve also debunked common myths and misconceptions surrounding scabies. We’ve highlighted the importance of early diagnosis and treatment. For more informative articles on skin health and other related topics, be sure to check out other resources on our site. Equipping yourself with knowledge is the first step in taking control of scabies transmission.
.