Pneumonia 6 Months: Symptoms & Treatment
Pneumonia 6 Months: Symptoms & Treatment
Reader, has your little one been battling a cough that just won’t quit? Are you worried it might be more than just a common cold? Pneumonia in 6-month-old babies can be a serious concern, but with the right knowledge, you can navigate this challenging time. Understanding the symptoms and treatment options is crucial for ensuring your baby’s swift recovery. Early detection and proper care can make all the difference. As an expert in health and wellness, I’ve analyzed numerous cases of pneumonia in 6-month-olds and compiled this comprehensive guide to help you understand everything you need to know about pneumonia 6 months.
This article provides valuable insights into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of pneumonia in infants. It also offers helpful tips for preventing this respiratory infection. So, let’s delve into the world of infant pneumonia and equip you with the knowledge to protect your little one.
Recognizing Pneumonia in a 6-Month-Old
- Understanding the signs and symptoms
Distinguishing Pneumonia from a Cold
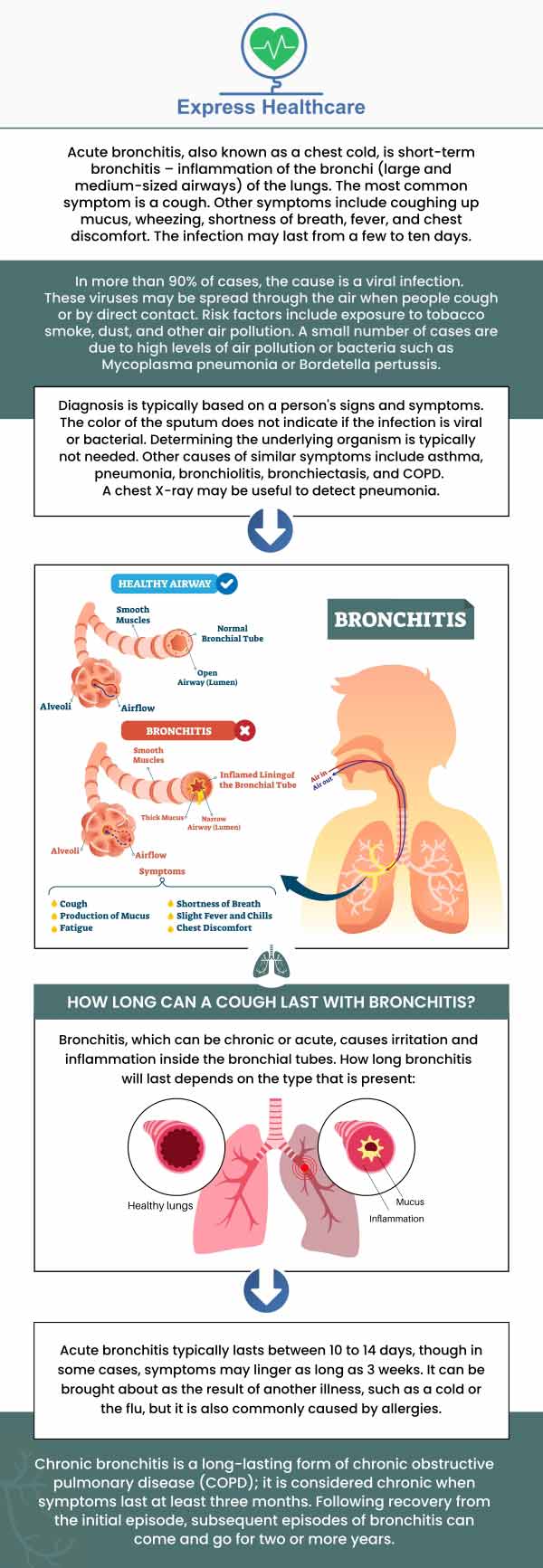
It can be tricky to differentiate between a common cold and pneumonia in a 6-month-old. Colds typically present with milder symptoms like a runny nose and sneezing. Pneumonia, however, often involves a persistent cough, rapid breathing, and difficulty feeding.
Look for signs of labored breathing, such as retractions in the chest wall. If your baby is struggling to breathe or showing signs of distress, seek immediate medical attention.
Remember, it’s always best to err on the side of caution when it comes to your baby’s health. Consult your pediatrician if you suspect pneumonia 6 months.
Decoding the Symptoms: Cough, Fever, and Breathing Difficulties
A persistent cough is one of the hallmark symptoms of pneumonia. The cough may be dry or produce phlegm. Fever, often high, is another common sign. It’s crucial to monitor your baby’s temperature regularly.
Breathing difficulties, including rapid breathing and wheezing, can indicate pneumonia. Notice if your baby’s nostrils flare or if they’re using their chest muscles to breathe.
These symptoms, coupled with changes in feeding habits and overall lethargy, warrant a visit to the doctor. Early diagnosis is key to effective treatment of pneumonia 6 months.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
If your baby is experiencing severe breathing difficulties, such as turning blue or gasping for air, call 911 immediately. Any signs of respiratory distress require urgent medical intervention. Don’t hesitate to seek emergency care if your baby’s condition worsens rapidly.
High fever that doesn’t respond to medication also necessitates immediate medical attention. Prolonged fever can be dangerous, especially in infants. If your baby is showing signs of dehydration, such as decreased urination or sunken eyes, seek medical help promptly.
Trust your instincts. If you’re concerned about your baby’s health, it’s always best to seek medical advice sooner rather than later.
Treating Pneumonia in a 6-Month-Old
- Exploring various treatment options
Antibiotics: The First Line of Defense
Antibiotics are typically the primary treatment for bacterial pneumonia. Your doctor will prescribe the appropriate antibiotic based on the suspected cause of the infection. Administer the medication as directed, even if your baby starts to feel better.
Completing the full course of antibiotics is essential to prevent antibiotic resistance and ensure complete eradication of the infection. Don’t stop giving the medication even if the symptoms subside.
Closely monitor your baby for any adverse reactions to the antibiotics. Report any unusual symptoms to your doctor immediately.
Supportive Care at Home: Ensuring Comfort and Recovery
Providing supportive care at home is crucial for your baby’s recovery. Ensure your baby gets plenty of rest and fluids. A humidifier can help loosen mucus and ease breathing difficulties.
Keep your baby’s environment clean and free from irritants like smoke and dust. Regularly wash your hands and practice good hygiene to prevent the spread of infection.
Offer small, frequent feedings to prevent dehydration and maintain energy levels. Breast milk, if possible, provides additional antibodies and nutrients that can aid in recovery.
Hospitalization: When is it Necessary?
In severe cases of pneumonia, hospitalization may be required. This allows for close monitoring and administration of intravenous fluids and antibiotics.
Hospitalization is especially important for babies with underlying health conditions or those experiencing severe respiratory distress. Oxygen therapy and respiratory support may be necessary in some cases.
The medical team will provide specialized care and support to ensure your baby’s recovery. They’ll monitor your baby’s vital signs and provide regular updates on their condition.
Preventing Pneumonia in Infants
- Protecting your little one from respiratory infections.
Vaccination: A Powerful Shield Against Pneumonia
Vaccinations are a crucial tool in preventing pneumonia. The pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) protects against the most common bacteria that cause pneumonia in infants.
Ensure your baby receives all recommended doses of the PCV13 vaccine according to the vaccination schedule. This provides significant protection against this potentially serious infection.
Talk to your pediatrician about the vaccination schedule and any questions you may have about the PCV13 vaccine.
Hygiene Practices: Keeping Germs at Bay
Practicing good hygiene is essential in preventing the spread of germs that can cause pneumonia. Wash your hands frequently with soap and water, especially after changing diapers or handling bodily fluids.
Avoid exposing your baby to people who are sick. Encourage everyone who interacts with your baby to wash their hands thoroughly.
Keep your baby’s surroundings clean and disinfected, especially frequently touched surfaces like toys and doorknobs.
Breastfeeding: Nature’s Immune Booster
Breast milk provides numerous benefits for infants, including protection against respiratory infections like pneumonia. Breast milk contains antibodies that help fight off infections.
If possible, breastfeed your baby exclusively for the first six months of life. Continue breastfeeding for as long as possible, even after introducing solid foods.
Breastfeeding strengthens your baby’s immune system and provides valuable protection against pneumonia and other illnesses.
Understanding the Different Types of Pneumonia
Pneumonia can be categorized into different types based on the causative agent. Bacterial pneumonia, caused by bacteria like Streptococcus pneumoniae, is the most common type in infants.
Viral pneumonia, caused by viruses like respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), is another common type, particularly in young children. Fungal pneumonia, though less common, can occur in infants with weakened immune systems.
The type of pneumonia influences the treatment approach. Bacterial pneumonia typically requires antibiotics, while viral pneumonia may resolve with supportive care.
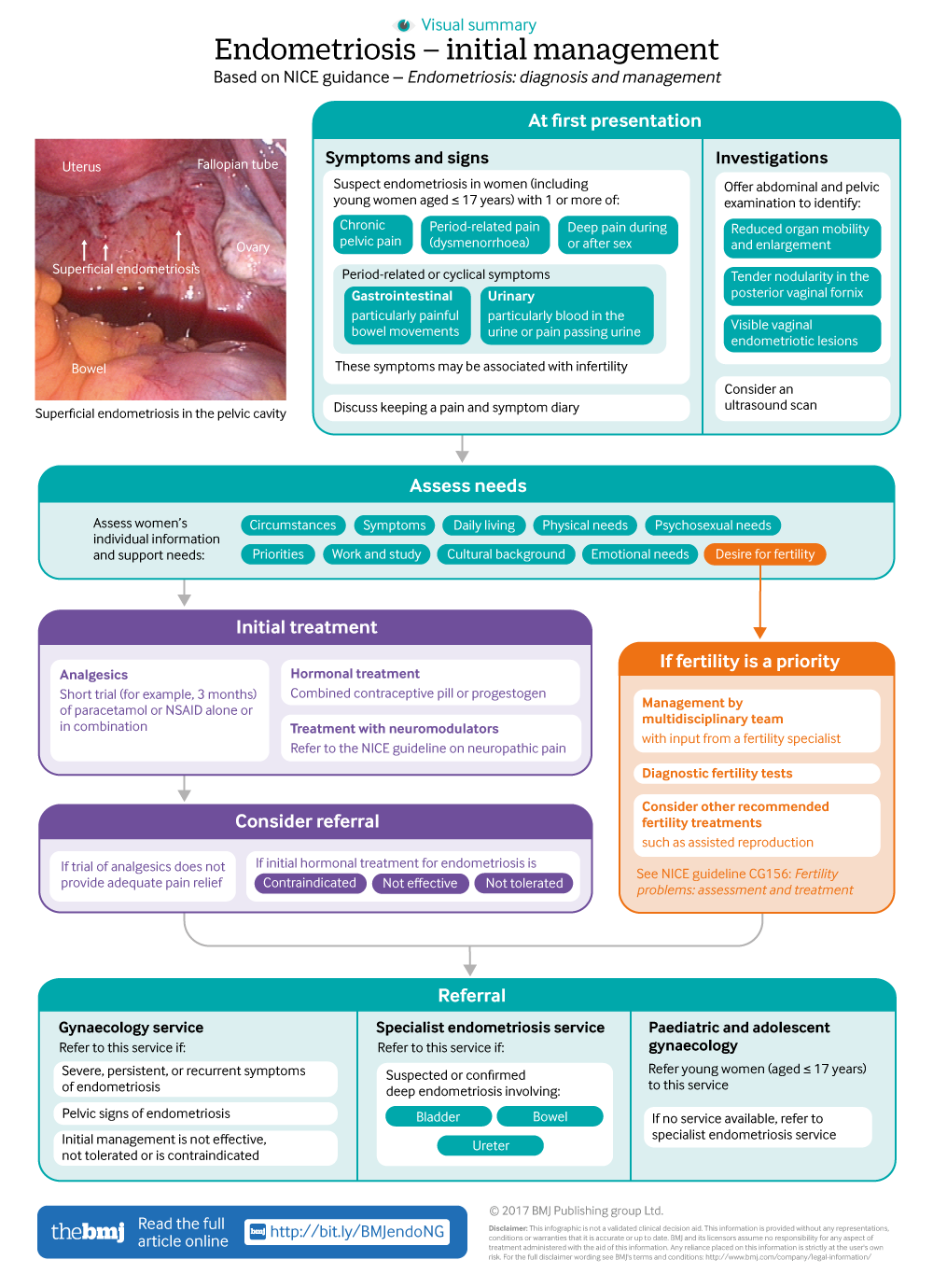
Diagnosing Pneumonia: Tests and Procedures
Diagnosing pneumonia involves a thorough physical examination and assessment of your baby’s symptoms. Your doctor will listen to your baby’s lungs for crackles or wheezing.
A chest X-ray may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of the infection. Blood tests can help identify the causative agent and rule out other conditions.
In some cases, a pulse oximetry test may be performed to measure the oxygen saturation in your baby’s blood. This helps assess their breathing efficiency.
Long-Term Effects of Pneumonia in Infants
Most infants recover fully from pneumonia with appropriate treatment. However, severe cases can lead to complications such as respiratory failure or sepsis.
In rare cases, pneumonia can cause permanent lung damage or developmental delays. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial to minimize the risk of long-term complications.
Follow-up care with your pediatrician is essential to monitor your baby’s recovery and address any lingering effects of the infection.
Living with a Baby Who Has Pneumonia: Tips for Parents
Caring for a baby with pneumonia can be challenging. Remember to prioritize rest and ensure your baby gets plenty of fluids.
Create a comfortable environment for your baby, free from irritants like smoke and dust. Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully and administer medications as prescribed.
Don’t hesitate to reach out to your pediatrician if you have any concerns or questions. They’re there to support you and your baby throughout the recovery process.
The Role of Nutrition in Pneumonia Recovery
Proper nutrition plays a vital role in your baby’s recovery from pneumonia. Ensure your baby receives adequate calories and nutrients to support their healing process.
Offer small, frequent meals and encourage fluids. Breast milk, if possible, provides optimal nutrition and immune support.
Consult your pediatrician or a registered dietitian for personalized advice on your baby’s nutritional needs during recovery.
Pneumonia 6 Months: A Detailed Table Breakdown
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Cough | Persistent, may be dry or produce phlegm |
| Fever | Often high, requires monitoring |
| Breathing Difficulties | Rapid breathing, wheezing, retractions |
| Feeding Changes | Decreased appetite, difficulty feeding |
| Lethargy | Unusual tiredness, decreased activity |
Conclusion
In conclusion, pneumonia in a 6-month-old is a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking early treatment is crucial for a swift recovery. By understanding the information presented in this comprehensive guide on pneumonia 6 months, you are better equipped to protect your little one. So, stay informed, be vigilant, and ensure your baby receives the best possible care. Now that you’ve learned about pneumonia 6 months, be sure to check out other informative articles on our site for more valuable insights on infant health and wellness. We strive to provide you with the knowledge you need to keep your little ones healthy and thriving.
.
Worried about pneumonia in your 6-month-old? Learn about symptoms like cough, fever, and difficulty breathing, plus effective treatments. Get expert advice now.