Diverticulitis & Xanax: Uses Side Effects & Safety
Diverticulitis & Xanax: Uses, Side Effects & Safety
Reader, have you ever wondered about the potential interactions between diverticulitis and Xanax? It’s a crucial topic for those managing diverticulitis while also dealing with anxiety. Understanding the implications of mixing these two can significantly impact your health. Navigating the complexities of medication interactions requires careful consideration. As an expert in this field, I’ve thoroughly analyzed the relationship between diverticulitis and Xanax, exploring its uses, side effects, and safety considerations. Let’s delve into this important discussion.
This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about your health. We will explore the intricacies of diverticulitis, the role of Xanax in managing anxiety, and the potential interplay between the two. This in-depth analysis addresses the crucial aspects of diverticulitis and Xanax.
Understanding Diverticulitis
Diverticulitis is a condition affecting the digestive system, specifically the large intestine. Small pouches, called diverticula, can form in the lining of the intestine and become inflamed or infected. This can lead to a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to severe abdominal pain. It’s important to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for diverticulitis.
What Causes Diverticulitis?
The exact cause of diverticulitis isn’t fully understood, but several factors contribute to its development. A low-fiber diet is often cited as a key risk factor, as it can lead to increased pressure within the colon. Aging also plays a role, with the condition becoming more common after age 40. Other factors, such as genetics and lifestyle choices, can also influence the likelihood of developing diverticulitis.
The pressure within the colon can cause the formation of the small pouches characteristic of this condition. These pouches, known as diverticula, can become inflamed or infected, leading to diverticulitis. Understanding these risk factors is crucial for prevention and management.
Maintaining a balanced diet rich in fiber can help prevent the formation of diverticula. Regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight can also contribute to overall digestive health, reducing the risk of diverticulitis.
Symptoms of Diverticulitis
The symptoms of diverticulitis can vary in severity. Some individuals may experience mild discomfort, while others face significant pain. Common symptoms include abdominal pain, typically on the lower left side, and changes in bowel habits, such as constipation or diarrhea.
Other symptoms may include fever, chills, nausea, and vomiting. If you experience any of these symptoms, especially severe abdominal pain, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications.
Prompt medical attention is vital for managing diverticulitis and preventing serious complications. Ignoring symptoms can lead to more severe issues, such as abscesses or perforations in the colon.
Treatment Options for Diverticulitis
Treatment for diverticulitis varies depending on the severity of the condition. Mild cases may be managed with rest, a liquid diet, and over-the-counter pain relievers. More severe cases may require antibiotics or even surgery.
In some instances, hospitalization may be necessary for intravenous antibiotics and pain management. For recurring or complicated cases, surgery may be recommended to remove the affected portion of the colon. Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential for determining the appropriate treatment plan.
A personalized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs is crucial for effectively managing diverticulitis. Your doctor will consider your overall health, the severity of your symptoms, and any underlying conditions when recommending a course of treatment.
Xanax: Uses, Side Effects & Precautions
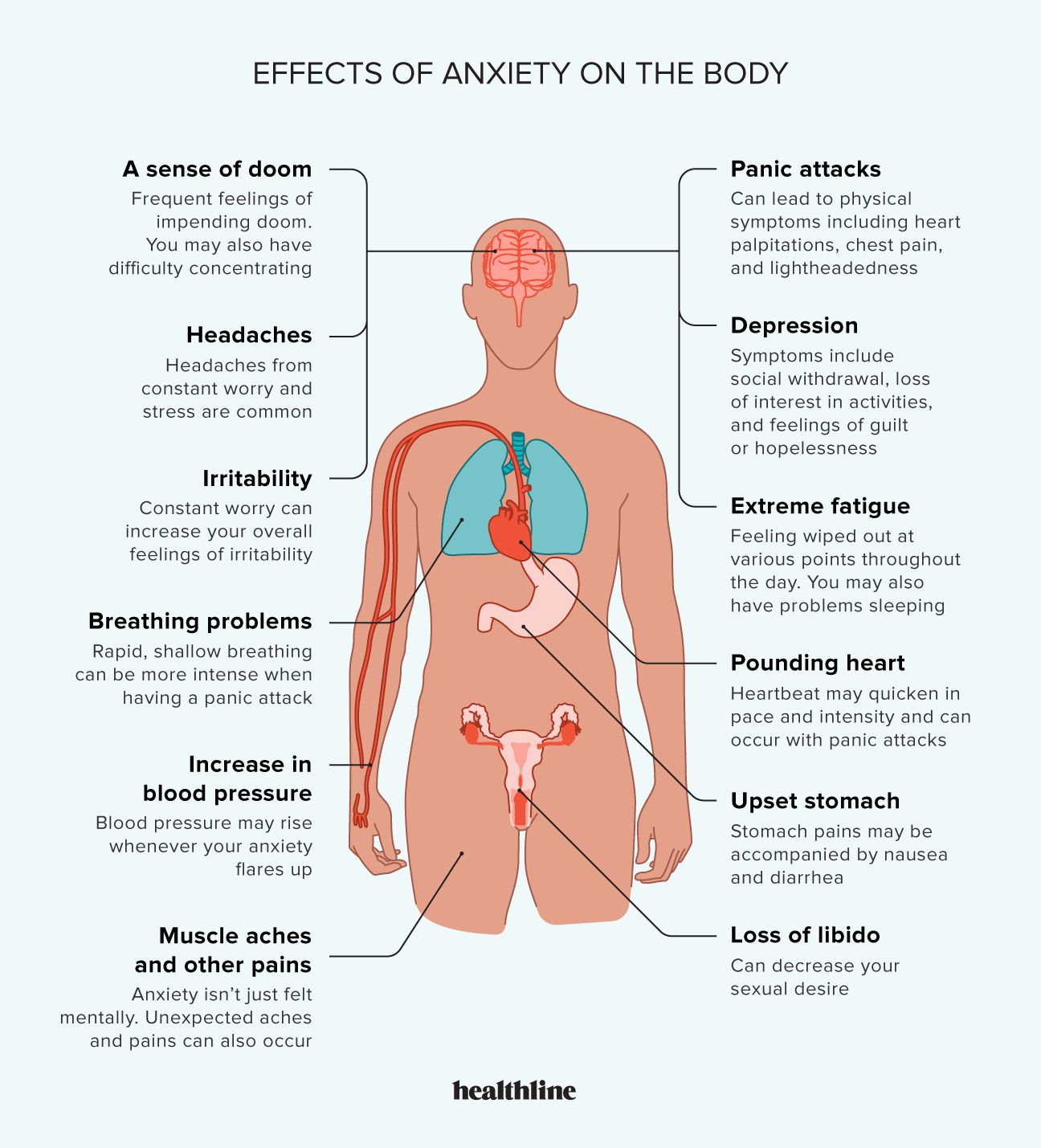
Xanax, also known as alprazolam, is a medication belonging to the benzodiazepine class. It’s primarily used to treat anxiety disorders and panic disorder. Understanding its uses, side effects, and precautions is essential for safe and effective use.
Understanding Xanax and its Uses
Xanax works by enhancing the effects of a neurotransmitter called GABA in the brain. This leads to a calming effect, reducing anxiety and promoting relaxation. It’s often prescribed for short-term use due to its potential for dependence.
While effective for managing anxiety, Xanax should be used cautiously and under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Long-term use can lead to tolerance and dependence, making it difficult to discontinue the medication. It’s important to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully.
Xanax can be beneficial for managing acute anxiety or panic attacks. However, it’s not a long-term solution for anxiety disorders. Therapy and other coping mechanisms are often recommended in conjunction with medication for long-term management.
Side Effects of Xanax
Like any medication, Xanax can cause side effects. Common side effects include drowsiness, dizziness, and impaired coordination. Some individuals may also experience changes in appetite, memory problems, or difficulty concentrating.
More serious side effects, though rare, can include confusion, hallucinations, and difficulty breathing. If you experience any unusual or concerning side effects, contact your doctor immediately. Monitoring for side effects is crucial for ensuring your safety.
It’s important to be aware of the potential side effects before starting Xanax. Discuss any concerns with your doctor, who can help you weigh the benefits and risks of the medication. Being informed empowers you to make the best decisions for your health.
Precautions and Warnings for Xanax Use
Certain precautions should be taken when using Xanax. It shouldn’t be combined with alcohol or other central nervous system depressants, as this can be dangerous. Individuals with certain medical conditions, such as liver or kidney disease, should use Xanax with caution.
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should also consult their doctor before using Xanax. The medication can be passed through breast milk and may harm the developing fetus. It’s crucial to discuss all medications with your healthcare provider during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Xanax can also interact with other medications, so it’s essential to inform your doctor about all the drugs you’re currently taking, including over-the-counter medications and supplements. This helps prevent potentially harmful interactions and ensures your safety.
Diverticulitis and Xanax: Potential Interactions
Understanding the potential interactions between diverticulitis and Xanax is crucial for managing both conditions effectively. While Xanax primarily addresses anxiety, it can indirectly influence diverticulitis symptoms. Let’s explore the multifaceted relationship between these two.
How Xanax Can Indirectly Affect Diverticulitis
Xanax, a central nervous system depressant, can slow down bowel movements. This can exacerbate constipation, a common symptom of diverticulitis. For individuals prone to constipation, using Xanax might worsen this symptom. Careful monitoring is advisable when using both.
Moreover, Xanax can sometimes mask the symptoms of diverticulitis, making it harder to detect a flare-up. This delayed recognition can potentially lead to complications if the diverticulitis worsens unnoticed. It’s important to be vigilant about any changes in your digestive health while taking Xanax.
While no direct interaction between Xanax and diverticulitis exists, the indirect effects on bowel movements warrant attention. Open communication with your doctor is essential to manage both conditions effectively and minimize potential complications. Addressing both anxiety and diverticulitis requires a holistic approach.
Managing Anxiety with Diverticulitis
Managing anxiety alongside diverticulitis requires a comprehensive approach. Stress can sometimes exacerbate diverticulitis symptoms, so it’s vital to manage stress effectively. Techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga can be helpful.
Beyond Xanax, other anxiety management strategies exist, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) or other medications. Exploring these alternatives with your healthcare provider can provide a more comprehensive solution for anxiety without potentially affecting diverticulitis.
Finding the right balance between managing anxiety and addressing diverticulitis symptoms is key. A collaborative approach with your healthcare provider ensures personalized care tailored to your specific needs. This approach considers both physical and mental health aspects for optimal well-being.
When to Consult a Doctor
If you experience worsening diverticulitis symptoms while taking Xanax, consult your doctor immediately. Open communication is vital for addressing potential complications promptly and adjusting treatment plans as needed. Don’t hesitate to seek advice when necessary.
.