Lyme Disease in Dogs: Symptoms & Treatment
Lyme Disease in Dogs: Symptoms & Treatment
Reader, have you ever wondered about the silent threat of Lyme disease lurking in your backyard, potentially affecting your beloved canine companion? Lyme disease in dogs is a serious concern, but with the right knowledge and proactive measures, you can protect your furry friend. Lyme disease, a tick-borne illness, can significantly impact a dog’s health, causing a range of debilitating symptoms. Early detection and treatment are crucial for preventing long-term complications. As an expert in this field, I’ve thoroughly analyzed Lyme disease in dogs, its symptoms, and effective treatment strategies.
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of Lyme disease in dogs, equipping you with the knowledge to identify, manage, and prevent this pervasive illness. We’ll explore the causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and available treatment options for Lyme disease in dogs.


Lyme disease is caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi and is transmitted through the bite of infected blacklegged ticks (also known as deer ticks). These tiny arachnids thrive in wooded and grassy areas, posing a risk to dogs who frequent these environments. Not all ticks carry the bacteria, and transmission typically requires the tick to be attached for at least 24-48 hours.
Understanding the lifecycle of the tick and the environmental factors that contribute to its prevalence is essential for preventing Lyme disease in dogs. Regular tick checks, especially after outdoor activities, are crucial. Prompt removal of attached ticks can significantly reduce the risk of transmission.
Preventing tick bites is the first line of defense against Lyme disease. This can be achieved through the use of tick preventatives, such as topical medications or oral chewables, and by maintaining a tick-free environment in your yard. Regularly mowing your lawn, removing leaf litter, and creating a barrier between wooded areas and your yard can help minimize tick populations.

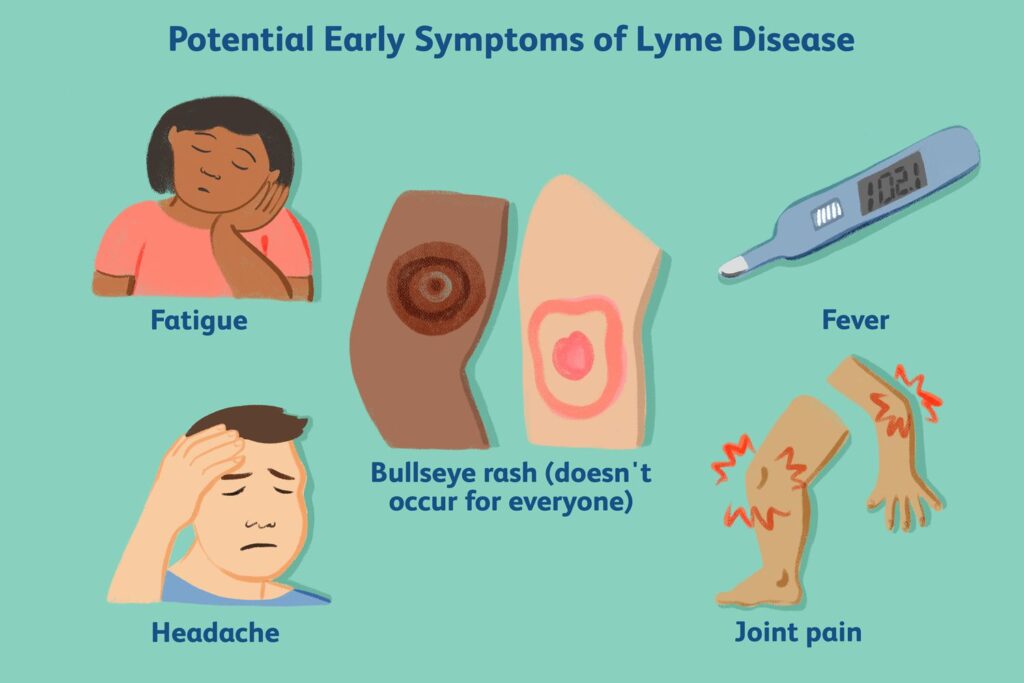
The symptoms of Lyme disease in dogs can vary widely, making early diagnosis challenging. Some dogs may not show any signs of illness for weeks or even months after infection, while others may develop acute symptoms within a few days. Common signs include lameness (often shifting between legs), fever, lethargy, loss of appetite, and swollen lymph nodes.
More severe symptoms, such as kidney problems, heart abnormalities, and neurological disorders, can occur in untreated cases. If your dog exhibits any of these symptoms, particularly after potential exposure to ticks, it’s crucial to consult a veterinarian immediately.
Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are essential for preventing the progression of Lyme disease and minimizing long-term health complications. The sooner treatment is initiated, the better the prognosis for a full recovery.

Diagnosis of Lyme Disease
Diagnosing Lyme disease in dogs involves a combination of factors, including the dog’s history of tick exposure, clinical signs, and laboratory testing. Blood tests can detect antibodies to the bacteria that cause Lyme disease. However, these tests aren’t always conclusive, especially in the early stages of infection.
Your veterinarian may recommend additional tests, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests, to confirm the diagnosis. A thorough evaluation of your dog’s overall health is essential to rule out other conditions with similar symptoms.
Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial for initiating appropriate treatment and preventing long-term complications associated with Lyme disease.
Treatment Options
The primary treatment for Lyme disease in dogs is antibiotics, typically doxycycline, administered for several weeks. The duration of treatment may vary depending on the severity of the infection and the individual dog’s response to therapy.
In some cases, supportive care, such as pain management and fluid therapy, may be necessary to alleviate symptoms and improve the dog’s overall well-being. Regular monitoring during and after treatment is important to ensure the infection has been eradicated and to address any potential complications.
While most dogs respond well to antibiotic treatment, some may experience persistent symptoms even after completing the course of medication. This is known as post-treatment Lyme disease syndrome (PTLDS) and requires ongoing management.
Lyme Disease Prevention Strategies
Preventing Lyme disease in dogs involves a multi-pronged approach. This includes regular tick checks, the use of tick preventatives, and maintaining a tick-free environment. Vaccinating your dog against Lyme disease is also an effective preventive measure.
The Lyme disease vaccine helps to stimulate the dog’s immune system to produce antibodies against the bacteria. This can reduce the risk of infection or lessen the severity of symptoms if infection does occur. It’s important to discuss vaccination with your veterinarian to determine the best course of action for your dog.
By implementing these preventive strategies, you can significantly reduce the risk of your dog contracting Lyme disease and protect their long-term health and well-being.
Living with Lyme Disease: Long-Term Management
For dogs who develop chronic Lyme disease or PTLDS, long-term management is essential to control symptoms and improve quality of life. This may involve ongoing medications, such as pain relievers or anti-inflammatories, and regular veterinary check-ups to monitor disease progression.
A healthy diet, regular exercise, and a supportive environment can also contribute to a dog’s overall well-being and help manage chronic symptoms. Working closely with your veterinarian to develop a personalized management plan is crucial for providing optimal care for your dog.
While Lyme disease can be a challenging condition to manage, with proper treatment and ongoing care, affected dogs can lead fulfilling lives. Early detection and intervention are key to minimizing long-term complications and ensuring a positive prognosis.
Detailed Breakdown of Lyme Disease in Dogs
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Cause | Borrelia burgdorferi bacteria transmitted by infected ticks |
| Transmission | Bite of infected blacklegged ticks (deer ticks) |
| Symptoms | Lameness, fever, lethargy, loss of appetite, swollen lymph nodes |
| Diagnosis | Blood tests, PCR tests, clinical signs, history of tick exposure |
| Treatment | Antibiotics (typically doxycycline), supportive care |
| Prevention | Tick checks, tick preventatives, vaccination, environmental control |
Frequently Asked Questions about Lyme Disease in Dogs
Can humans get Lyme disease from their dogs?
No, Lyme disease cannot be transmitted directly from dogs to humans. However, both dogs and humans can contract Lyme disease through the bite of an infected tick.
It’s essential to take precautions to protect both yourself and your dog from tick bites. This includes using tick preventatives, performing regular tick checks, and avoiding tick-infested areas.
By taking proactive measures, you can minimize the risk of Lyme disease for both you and your furry companion.
How effective is the Lyme disease vaccine for dogs?
The Lyme disease vaccine for dogs is considered effective in reducing the risk of infection and lessening the severity of symptoms if infection does occur. However, no vaccine is 100% effective.
It’s essential to discuss vaccination with your veterinarian to determine the best course of action for your dog based on their individual risk factors. Even with vaccination, other preventive measures, such as tick control, should be implemented.
Combining vaccination with other preventive strategies provides the most comprehensive protection against Lyme disease in dogs.
Conclusion
Therefore, understanding Lyme disease in dogs, its symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for responsible pet ownership. Early detection and prompt treatment are essential for preventing long-term complications and ensuring a positive outcome.
By implementing preventive measures and working closely with your veterinarian, you can protect your canine companion from this debilitating disease. For more informative articles on pet health and wellness, be sure to check out other resources on our site. Lyme disease in dogs is a serious concern, so stay informed and proactive.
.
Protect your pup from Lyme disease. Learn to spot the symptoms & get effective treatment. Keep your dog healthy & happy!